Document semi-structured (JSON, XML) data in relational databases
NoSQL revolution has got its way into the relational world. You may be working with relational databases and still have to query and understand semi-structured data, hidden in text columns, in JSON or XML documents.
The hidden data complexity
Let us have a look at the following table that we used to import data from Calendly (online meeting booking software):
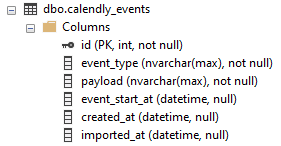
On the surface, it looks simple, just five columns. But if you look inside, you will notice that two of the columns are in fact (JSON) document stores.
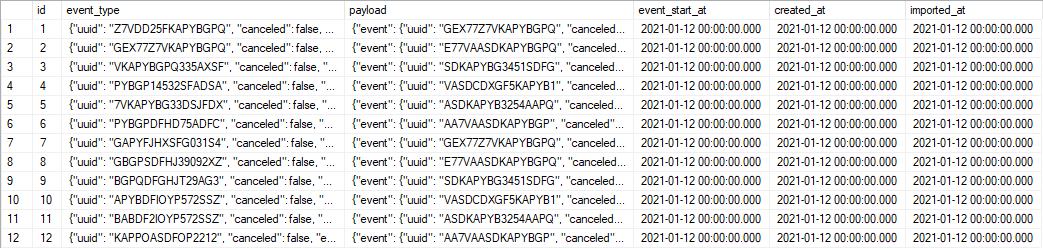
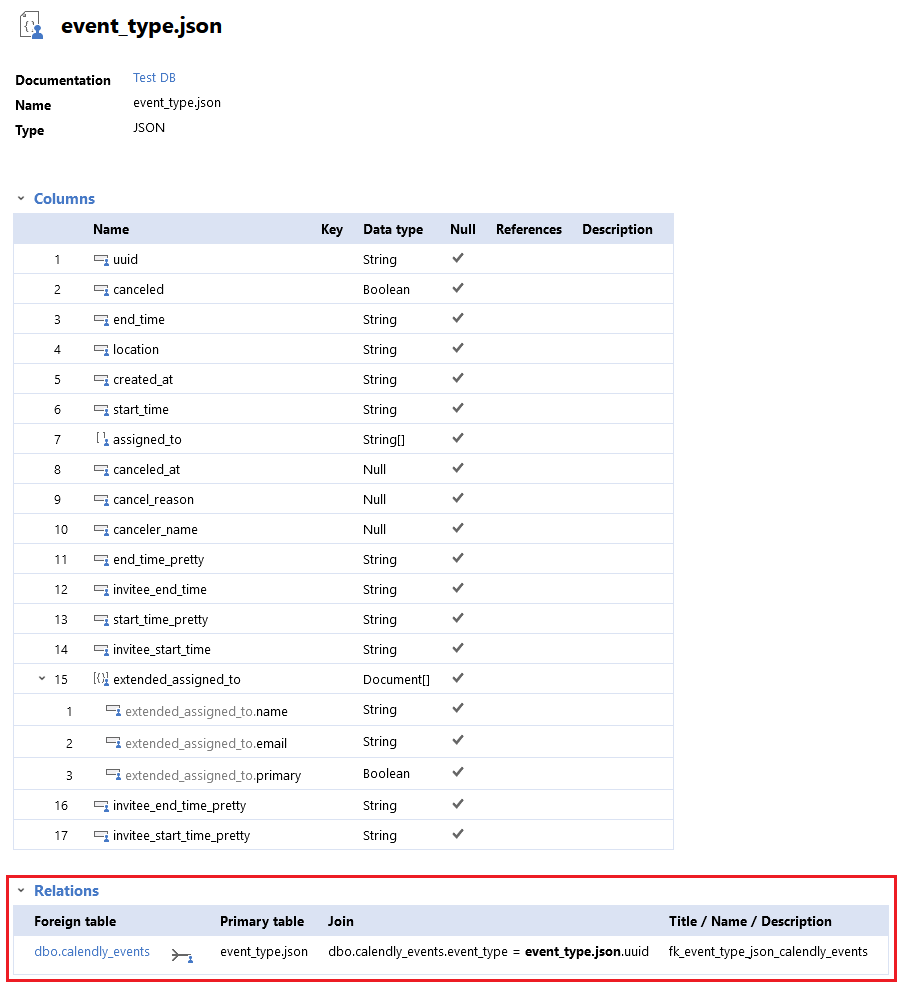
If you look into the documents, you will see that the majority of the fields and complexity of the data model is hidden inside those two text columns. Therefore, to understand the data structure it is not enough just to see the list of columns, you must also understand the structure of the JSON documents inside this data.

Document JSON
I have good news - Dataedo can help you with that. You are able to automatically extract and document the structure of JSON documents and link them to table columns.
First, you need to add the JSON document to the catalog. Click on the database in the repository navigator, choose Add Object, and Add/Import Structure.
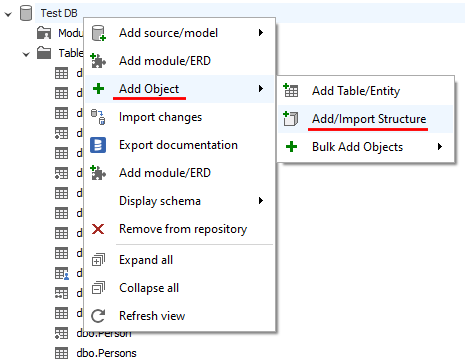
Then choose the Paste Document option to be able to parse JSON automatically.
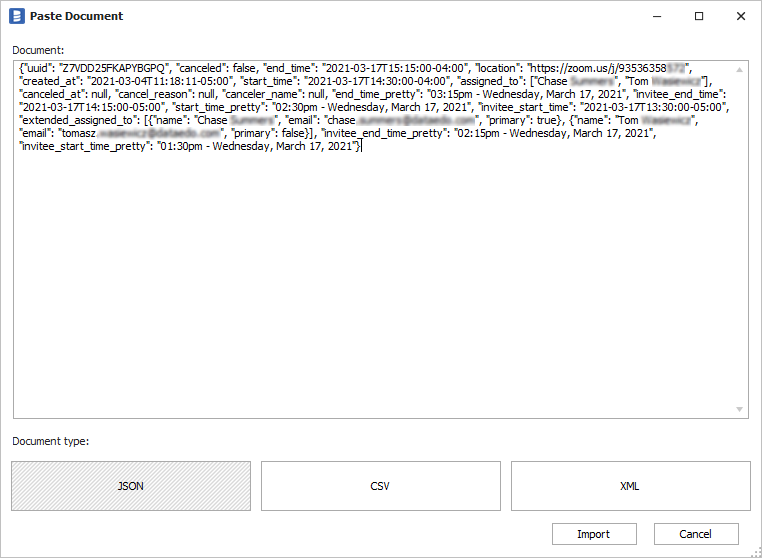
Now, paste any JSON document from the column. It should be representative, i.e., have all (or the majority) of the fields. If it's a correct document, then you will notice that Dataedo detects the format as JSON. Click Import to add the structure of the document.
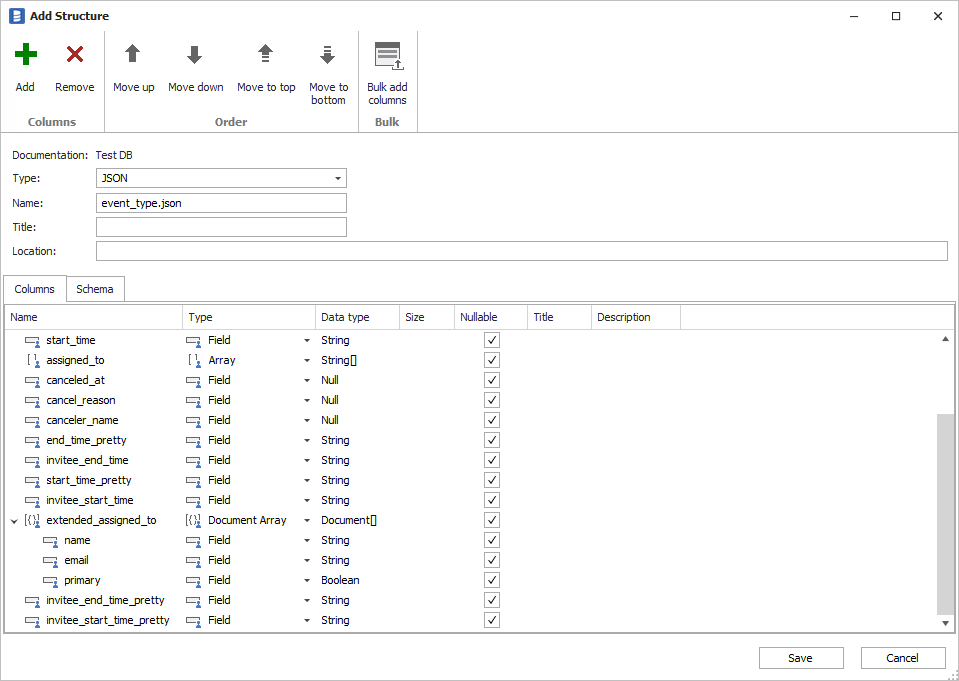
Dataedo will open a window with the structure of the parsed document. This is where you can modify it (it will also be available after you add it to the repository) - add, rename, or remove fields or change types. Provide a name for the structure - it is a good practice to include the format, e.g., event_type.json.
Now you can save the new structure to the repository.
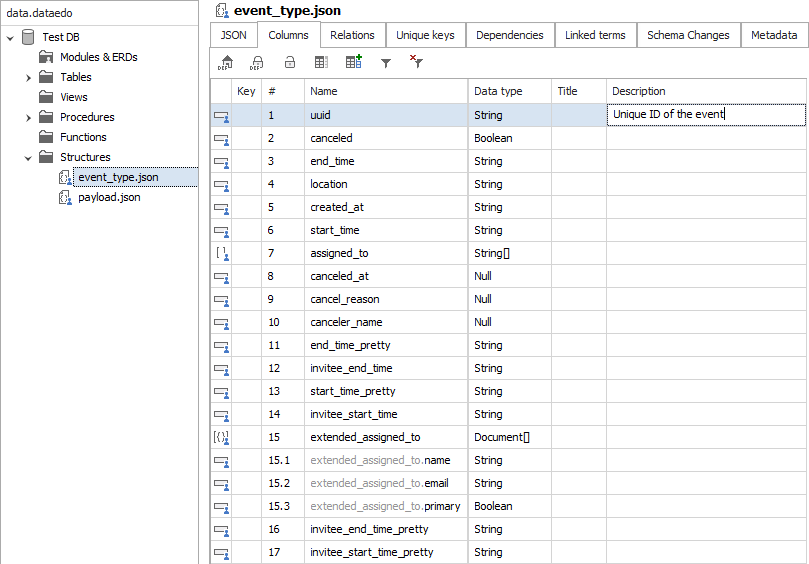
This will create a new folder named Structures with the newly added structure. You can browse their fields just as you do for any other objects. You can also document the fields using description, title, or custom fields.
Linking documents and columns
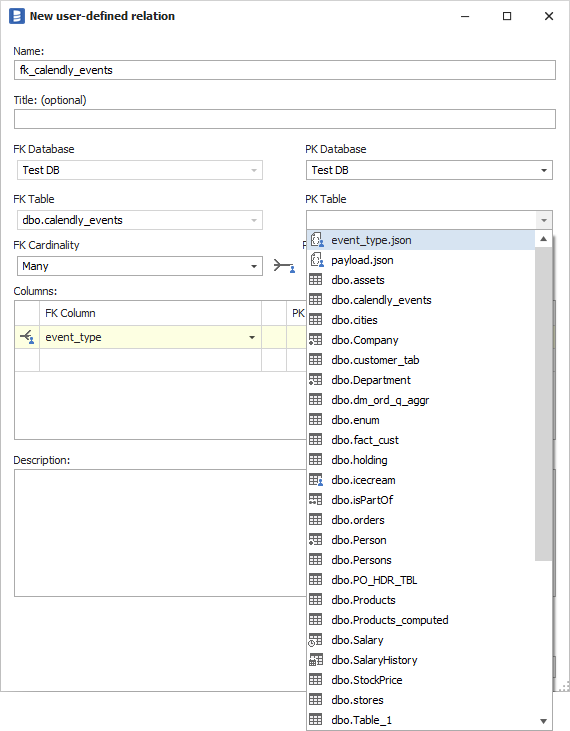
OK, so you have documentation of the JSON document. Now, you need to specify that table columns hold specific documents. To do it you can use a manual relationship (used mainly to define foreign keys/joins). Right-click on the column and choose Add relation. Now in the PK Table field choose the relevant document from the list, select PK (or any other) column in the PK Column field and save the relationship.
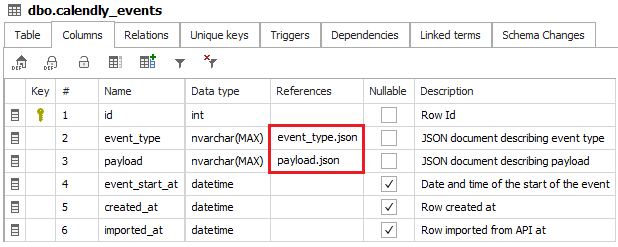
You will notice referenced documents in the References column. You can also find those links on the Relations tab.
End result
Your job is complete. You documented JSON documents stored in your database and explained which fields hold those documents. This approach allows you to link one document to multiple columns.
Below is the view from the HTML documentation. You will notice that it's easy to see that columns hold documents and navigate to their definitions.
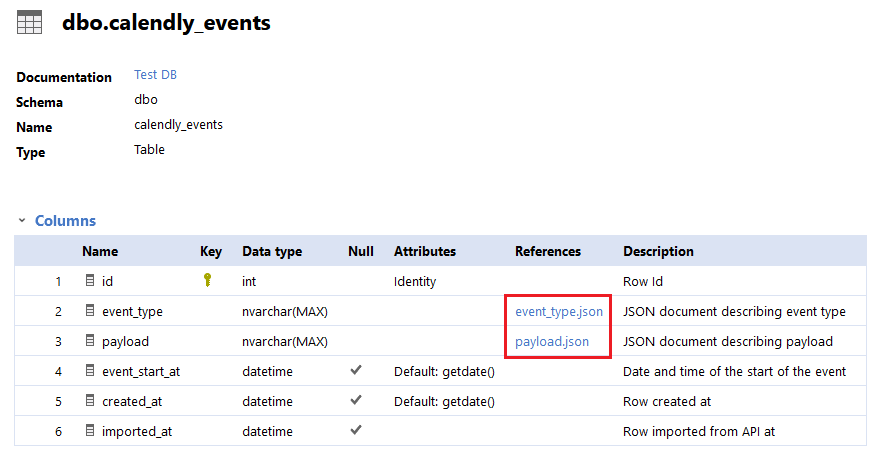
It is also easy to find out where a specific document is used in your database.