Connecting to PostgreSQL database
PostgreSQL is one of the most advanced open-source relational databases. Dataedo provides a native connector to PostgreSQL with SSL support.
PostgreSQL SSL configuration
Generating certificates
Server configuration and generating SSL certificates for a server is described in official PostgreSQL documentation - Secure TCP/IP Connections with SSL section.
Following sections (Converting client certificate to PFX format and Add certificate to a trusted root authorities store) are both optional, and can be ignored if you authenticate with a password and not with the client certificate.
Converting client certificate to PFX format (optional)
Dataedo requires client certificate to have .PFX format (so that both certificate and private key are in the same file). If you have client certificate in formats such as PEM, CRT, CER or others, they won't be accepted by Dataedo. However, you can easily convert existing certificates into PFX certificate using the following OpenSSL command:
openssl pkcs12 -export -out client-cert.pfx -inkey private-key.key -in client-cert.crt
- openssl - command to execute OpenSSL,
- pkcs12 - file utility,
- -export -out client-cert.pfx - export and save the certificate as PFX client-cert.pfx file,
- -inkey private-key.key - the private key to be combined with certificate into PFX file,
- -in client-cert.crt - client certificate to be combined with private key into PFX file.
OpenSSL then asks you to provide a passphrase to protect the file. You can leave it empty, although we recommend setting a safe password, as having a certificate may allow anyone to connect to a database.
Add certificate to a trusted root authorities store (optional)
If your server uses a self-signed certificate or one that was issued by an organization not considered as trusted by Microsoft (you can find the full list in documentation) and you want to use Verify CA or Verify Full SSL mode (see more in Connection Details section), you need to add a CA certificate (this can be provided by a database administrator) to your trusted root certificates store.
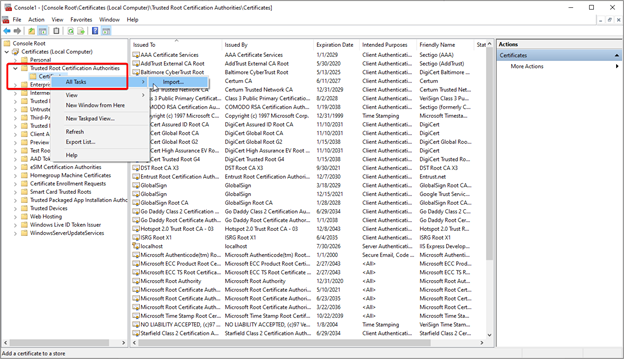
To do this, run Microsoft Management Console as an administrator - type mmc in the start menu, right-click the icon, and choose Run as Administrator.
Then expand the Console Root, Certificates (Local Computer), and Trusted Root Authorities Store. Right-click on Certificates. Choose All Tasks > Import and select the CA file.
Importing Metadata in Dataedo Portal
Entry point
To start the Metadata Import flow, make sure you have the Connection Manager role.
Then navigate to:
Connections → Add new connection → PostgreSQL
This will open the import wizard described in the following steps.


Step 1. Host details
Provide the connection details such as host, port, and SSL mode.
You will also be asked to name the Connection.
A Connection in Dataedo represents a saved configuration for accessing a data source.
It can be reused for future imports and scheduling.

Step 2. Credentials
Choose credentials from the list of existing ones available for the selected connector, or add new credentials.

Step 3. Databases
- The Portal will display all databases accessible with the provided credentials.
- You can select multiple databases at once and use the search box to narrow down results.
- Each selected database should be given a Title, which will be visible in Dataedo.
- At this step, the Portal also retrieves the number of assets in each source.

Step 4. Objects to import
For each selected database, you can refine which objects to import:
- Select schemas and object types (tables, views, procedures, etc.).

- Use Advanced filters to include or exclude objects with:
- schema patterns
- name patterns


Step 5. Schedule
Configure scheduling options for each source individually:
- Define tasks you want to schedule (Metadata Import, Data Quality run, Refresh Profiling).
- Run daily, on selected weekdays, or on specific days of the month.
- Choose an exact time of execution.
- Task state:
Active– the task will run as scheduled.Draft– the task is saved but not executed until switched to Active.
- Run immediately – when checked, the task will also be executed right after clicking
Create connection.
Only one source in a metadata import can have Run immediately selected.


You must configure at least one import task in the schedule section.
If you skip this, an empty database will be created and no metadata will be imported.
Importing Metadata in Dataedo Desktop
Metadata import is also possible using Dataedo Desktop.
In this mode, you can only import one source at a time.
Add new connection
To connect to PostgreSQL database create new documentation by clicking Add documentation and choosing Database connection.
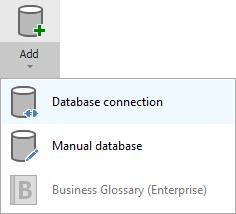
On the connection screen choose PostgreSQL as DBMS.
Connection details
Provide database connection details:
- Host - provide a host name or address where a database is on. E.g. server17, server17.ourdomain.com or 192.168.0.37.
- Port - change the default port of PostgreSQL instance if required.
- User and password - provide your username and password.
- SSL Mode - select the SSL Mode for connection:
- Prefer - Dataedo first will try to connect to a database with SSL support, and in case it didn't work it will try to establish a connection without SSL encryption.
- Disable - connection will be unencrypted.
- Require - only encrypted connection is possible.
- Verify CA - connection will be encrypted and Dataedo will verify if a server certificate was issued by a trusted authority.
- Verify Full - connection will be encrypted, Dataedo will verify if a server certificate was issued by a trusted authority and if all the information provided in the certificate are correct.
- Configure SSL - optional step if you want to authenticate with a client certificate.
- Database - type in database name or click [...] and choose it from the list.
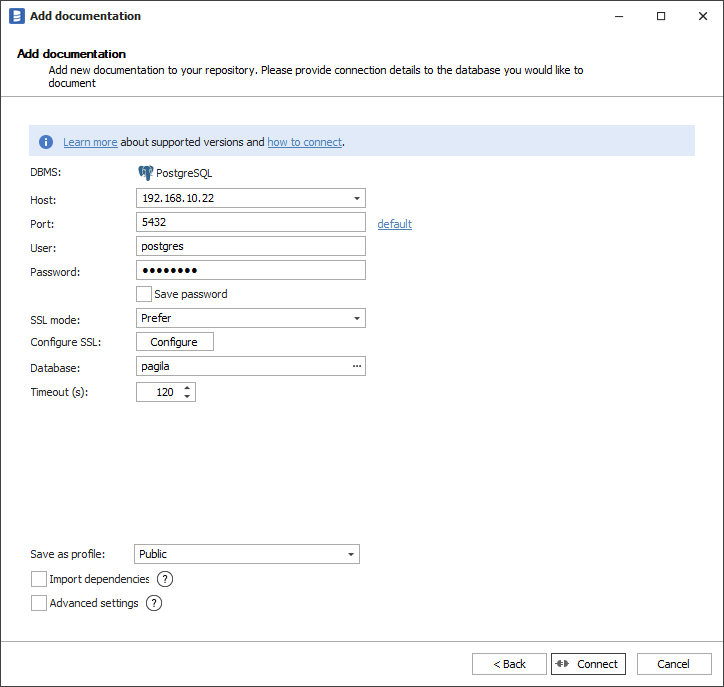
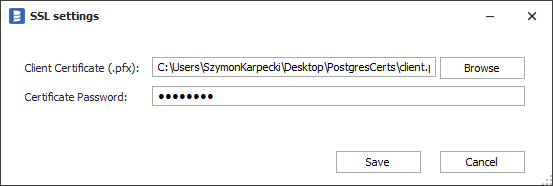
To add a client certificate for a connection, click the Configure button and choose the certificate file. If your certificate is protected with a passphrase, provide it in the Certificate Password field. Otherwise, leave the field empty.
Saving password
You can save the password for later connections by checking the Save password option. Passwords are saved in the repository database.
Importing schema
When the connection is successful, Dataedo will read objects and show a list of objects found. You can choose which objects to import. You can also use advanced filter to narrow down the list of objects.
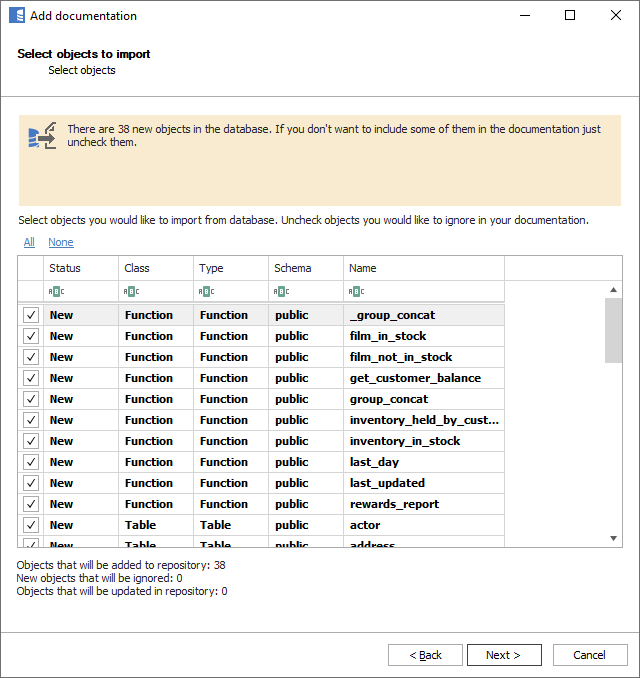
Confirm the list of objects to import by clicking Next.
The next screen will allow you to change the default name of the documentation under which your schema will be visible in the Dataedo repository.
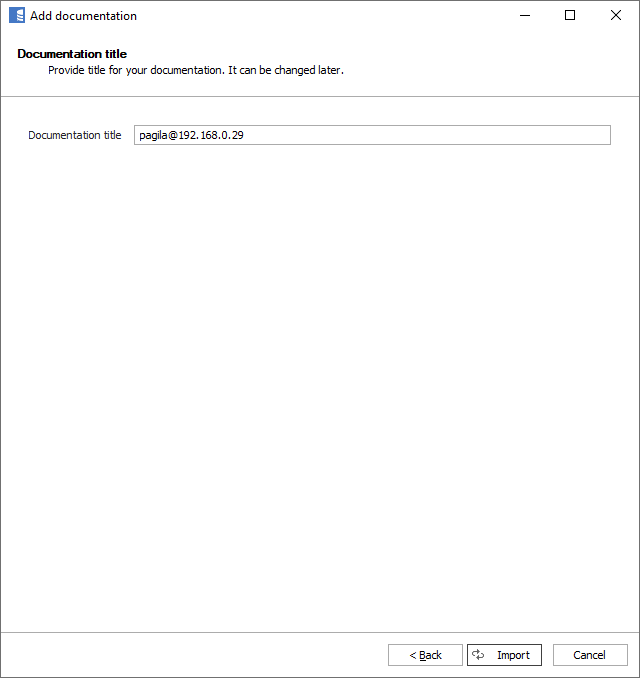
Click Import to start the import.
When done, close the import window with the Finish button.
Outcome
Your database schema has been imported to new documentation in the repository.
Permissions
To perform a PostgreSQL import, the role that performs it must have permissions to perform SELECT on the following objects:
- pg_catalog.pg_namespace
- pg_catalog.pg_class
- pg_catalog.pg_proc
- pg_catalog.pg_views
- pg_catalog.pg_matviews
- pg_catalog.pg_description
- pg_catalog.pg_language
- pg_catalog.pg_index
- pg_catalog.pg_attrdef
- pg_catalog.pg_trigger
- pg_catalog.pg_constraint
- pg_catalog.pg_attribute
If you use version 10 or higher, you must also have permissions to perform SELECT on the following objects:
- pg_catalog.pg_type
If you use version below 10, you must also have permissions to perform SELECT on the following objects:
- information_schema.table_constraints
- information_schema.parameters
- information_schema.key_column_usage
- information_schema.routines
To import dependencies, the role that performs the import must have permissions to perform SELECT on the following objects:
- pg_catalog.pg_rewrite
- pg_catalog.pg_depend
Dataedo also need access to catalog functions like pg_get_functiondef.
Additionally, the role that performs the import must have USAGE on the schema that you want to document or other access rights to objects that you want to document.
PostgreSQL support
Learn more about PostgreSQL support in Dataedo.

