Importing changes from database
When your database schema changes, you can import those changes and update your Dataedo documentation schema in a similar way you imported it.
Import changes
To update documentation, click the Import changes button in the ribbon.
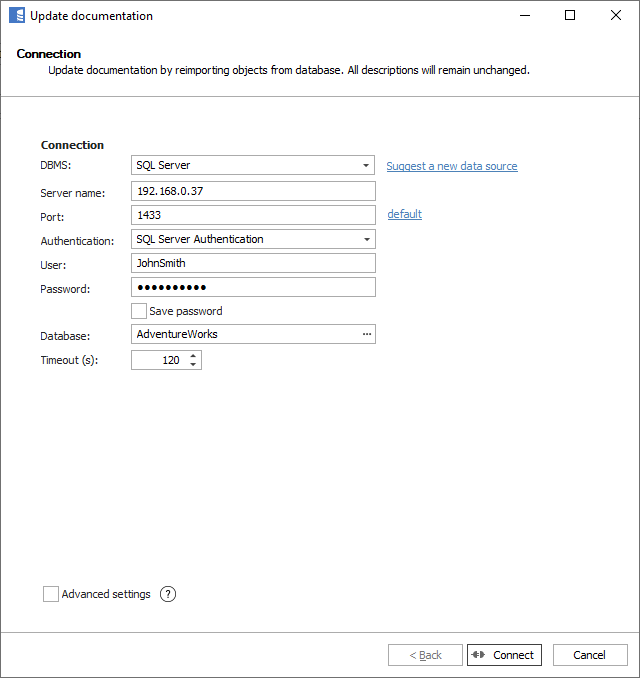
This will open the update wizard. The first screen is a connection form. Connection details are populated from the last connection - at import or last update. If you didn't use the 'Save password' option at the last connection, then you need to enter the password.
You can change connection details to point to a different database (even on a different server). In this case, use the 'Reimport all objects' option that is available in the next step. This may cover scenarios where you migrated databases to a new location or you want to switch between Dev, Test, and Live environments.
By default, the import will use the same filter you used last time. To change the filter, check the Advanced options box.
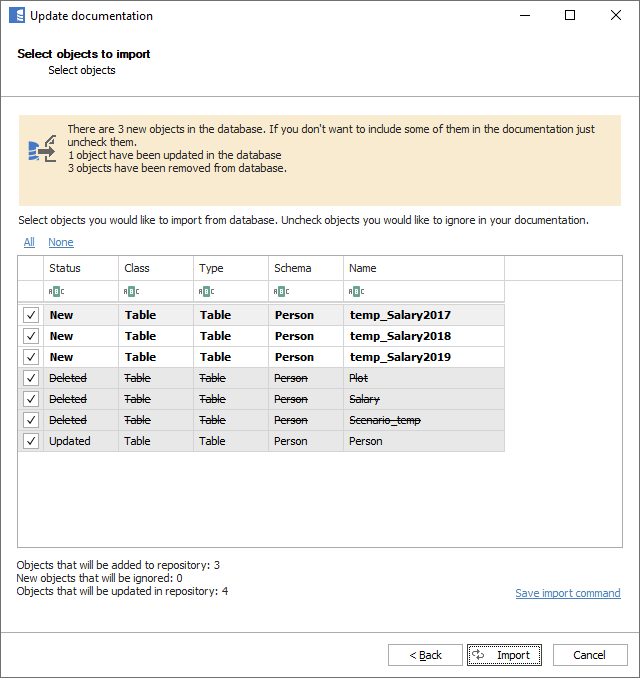
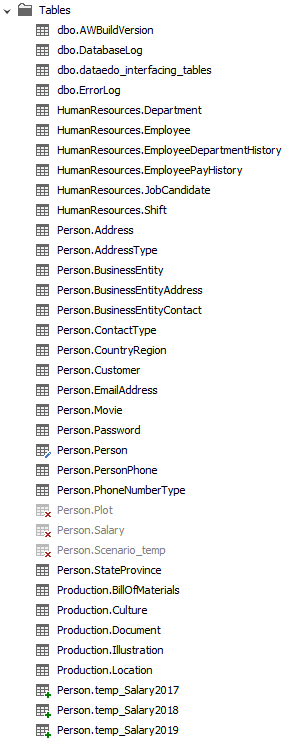
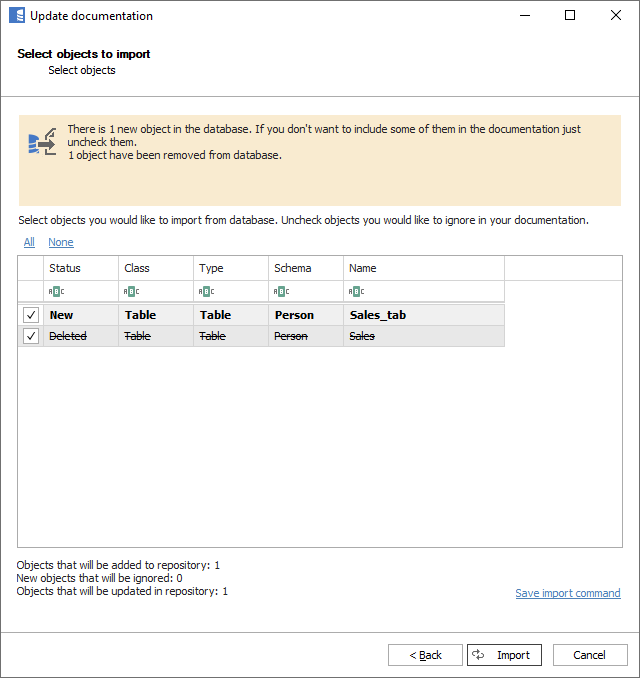
The next form will present changes in the database schema since the last import. You may choose to exclude some of the new objects from importing by unchecking them. You may also choose to include previously ignored objects by checking them.
The list shows:
- New - objects that were added to the schema since the last import
- Deleted - objects that were deleted from the schema since the last import
- Updated - objects that were updated since the last import (e.g., a column was added)
- Ignored - objects previously ignored from import
To import changes, click the Import button.
After the update, all new, updated, and deleted objects in the navigation tree will be marked with icons.
How it works
Dataedo gets (filtered) a list of objects (tables, views, stored procedures, and functions) from the server with the last modification date (this does not include MySQL - see details in the chapter below). Then it compares the list by names with the list from the repository. Objects that do not exist in the repository are considered new, objects that do not exist in the database are considered deleted. Objects whose names match but the server modification date is newer than the one in the repository (dbms_last_modification_date column) are considered updated.
New objects
New objects are simply added to the repository.
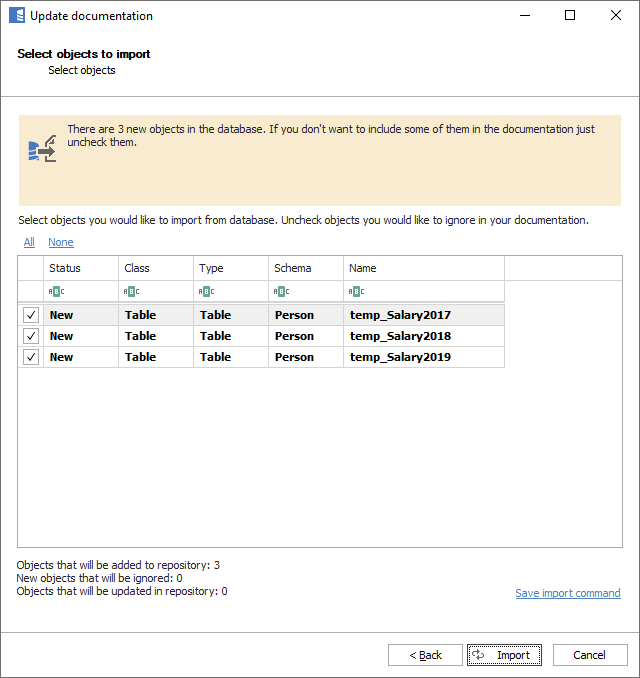
New objects are marked with star icons in the navigation tree. The icon disappears after the view gets refreshed.
Handling schema changes
Sometimes objects or columns in your database get dropped. After you import changes to Dataedo, those objects/columns will be marked accordingly.
Deleted objects
After an object in the database (table, stored procedure, etc.) gets dropped, when importing changes, Dataedo lists those in the import wizard.
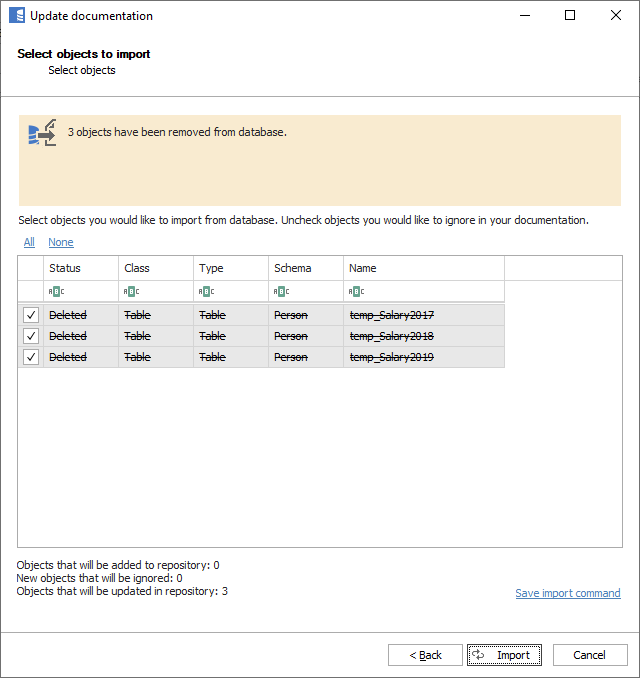
Deleted objects are marked as deleted but are still visible in the editor. All content is preserved. You may preview such objects and decide to delete them permanently from the repository - all content will be lost.
Deleted objects are marked with red cross icons in the navigation tree.

Deleted objects and their elements are ignored from all exports.
Once you delete the object from the repository, its name gets added to the list of ignored objects. If an object with that name is created again, it will be ignored in future imports. Read more about ignoring and removing objects from documentation.
Deleted columns, keys, etc.
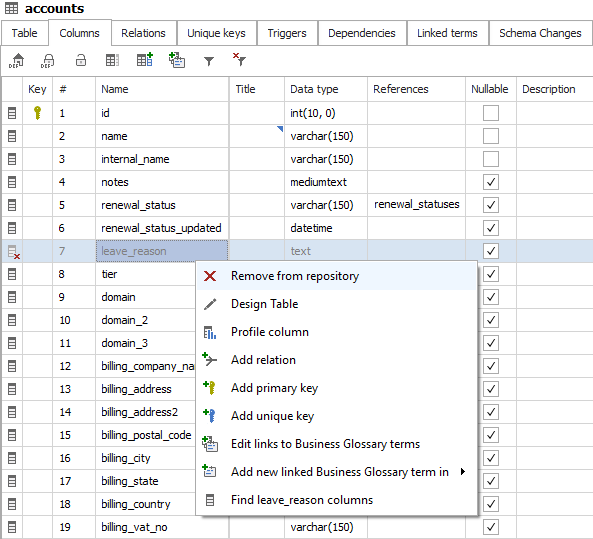
Similarly to objects (tables, views, etc.), their elements (columns, keys, parameters, etc.) are marked as deleted when missing in import. The idea is the same - copy the description and delete with the Delete key or Remove from repository option in the context menu (right-click).
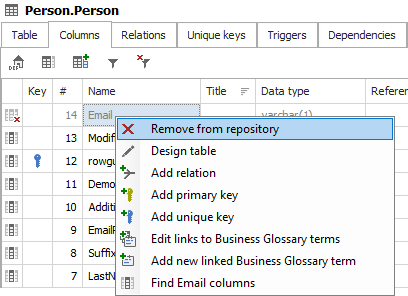
Removing deleted objects from the repository
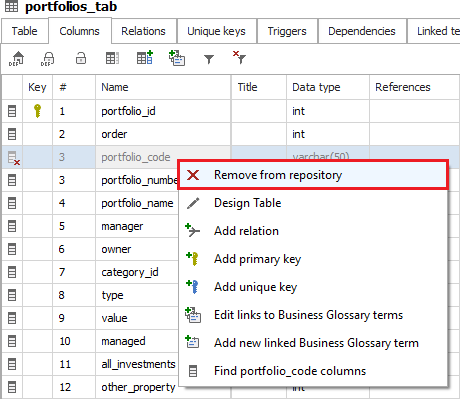
If you decide that you don't want a specific object or column in the repository, you can remove it. To remove an object, select the object from the navigation explorer, right-click, and choose the Remove from repository option or press the Remove button in the ribbon.
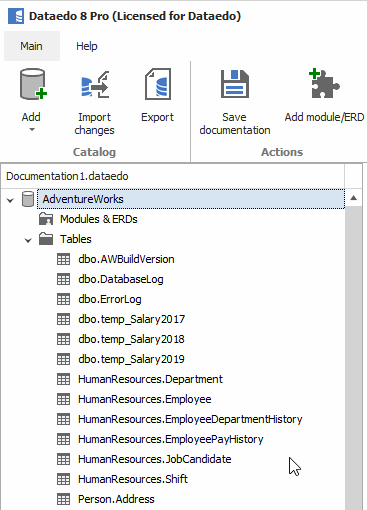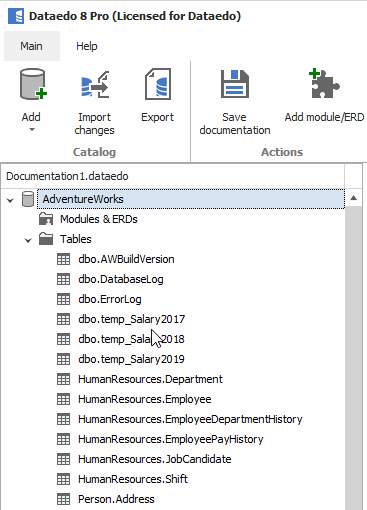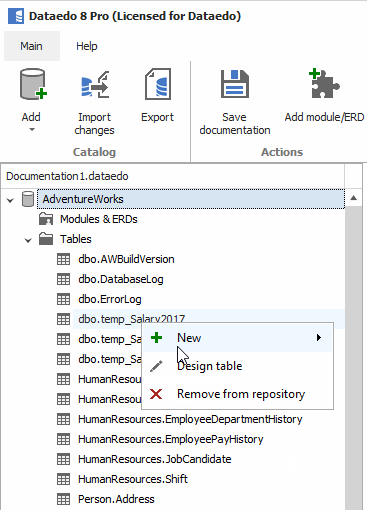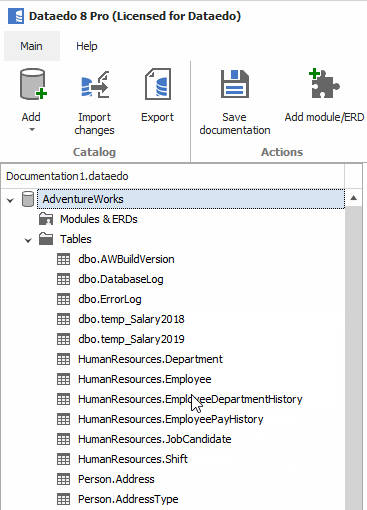
Objects that get deleted (their names) are added to the ignored objects list.
Removing deleted columns from the repository
To remove a deleted column, you can select it in the Columns tab and choose the Remove from repository option.
Renamed objects
When an object is renamed in the database, Dataedo behaves just as if it was deleted and created with a new name.
It marks the object with the old name as deleted and creates a new one with the new name.

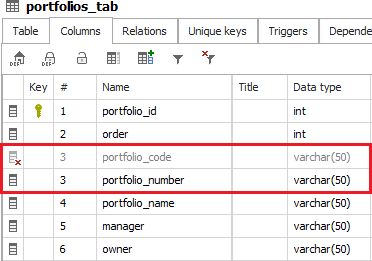
Renamed columns, keys, etc.
Renamed columns (and keys, parameters, etc.) work the same as objects - an element with an old name gets marked as deleted, and an element with a new name is created. And again, copy the description from the old to the new element if required and delete the old element.
Cleansing documentation - renamed objects
After the change, you will end up with two objects in the repository. You may want to:
- Copy documentation (manually) from the old to the new object.
- Remove the old object from the repository.
Cleansing documentation - renamed columns
Similarly to objects, you might want to:
- Copy the description and other fields from the old to the new column.
- Remove the old column from the repository.
Renaming objects manually
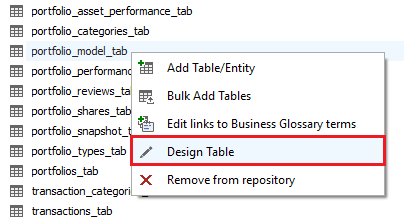
You can avoid the hassle of copying the description from the old to the new object if you know (before the import) that the object name changed. You can use the design option to rename the object in the repository to match the name (and schema) in the database.
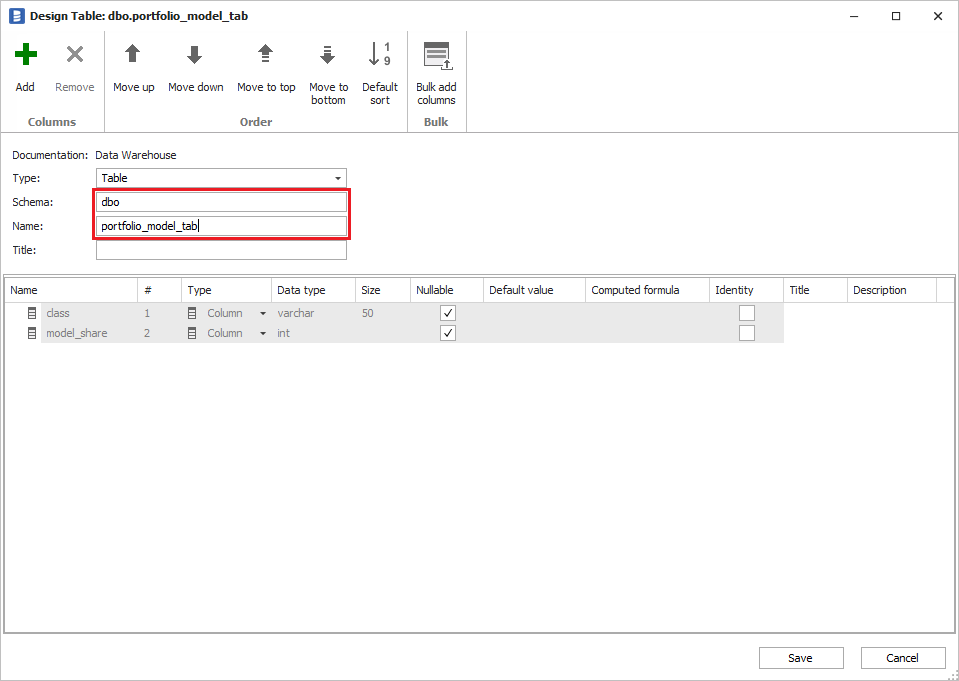
This object will be changed to manual. It will switch to physical during import.
Full reimport
When updating documentation to shorten schema importing time, Dataedo imports only objects that were changed since the previous update.
Sometimes, you may want to update object metadata in Dataedo even if it was unchanged in the source database.
This feature may also be referred to as Full reimport or Force reimport.
Mandatory Force reimport
Some database engines do not provide timestamps of schema objects' last updates, so Dataedo must perform a full reimport each time (force full import checkbox is always selected).

This mode will not cause any problems, but it takes a little longer since all objects need to be read.
These database engines are:
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- Percona for MySQL
- Amazon Aurora MySQL compatible
When to force a reimport of all objects
Depending on the database provider, some changes may not change the last edited timestamp on objects. For example, editing an extended property is not considered a change on the parent object in SQL Server.
Additionally, sometimes new features added in Dataedo may require reimporting objects imported through older versions (this was the case, for example, when we added dependencies).
When you run into issues in documentation imported originally in previous Dataedo versions, we strongly recommend running a forced reimport.
How to run a reimport of all objects
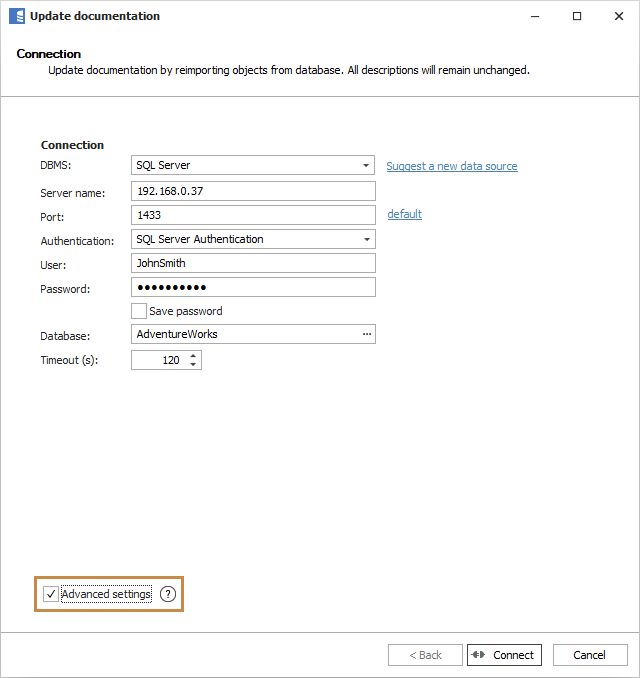
After highlighting the documentation you want to update, click the Import changes button in the ribbon.

On the first screen, check the Advanced settings box.
If you're importing data from SQL Server and have any custom fields, you may see an additional screen containing extended property to custom fields mapping. Ignore it for now.
When you get to the Include/Exclude objects screen, make sure the filter includes all the objects you want to update and check the Reimport all included objects box.
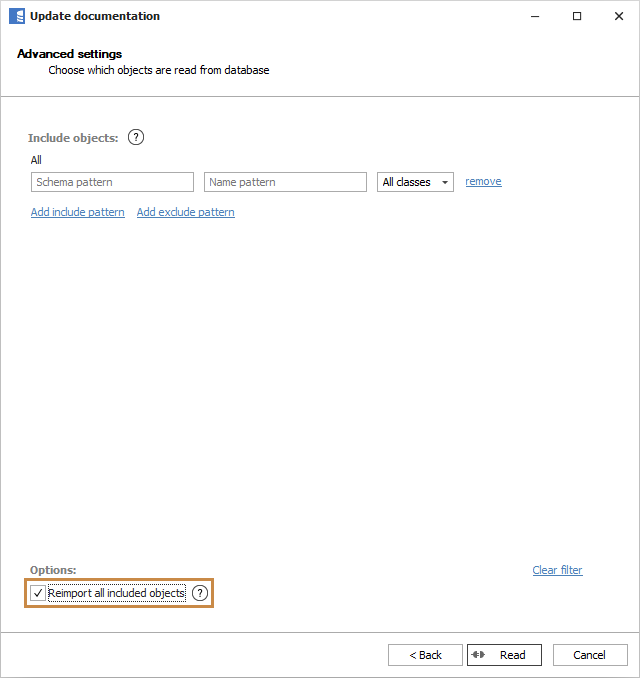
Click the Read button and wait for the operation to finish - it may take longer than usual updates, so please be patient. When the operation finishes, all your objects will be up to date.