Command line
Dataedo includes a feature to update or export documentation from the command line. To do so, you must first create a command file.
Command file
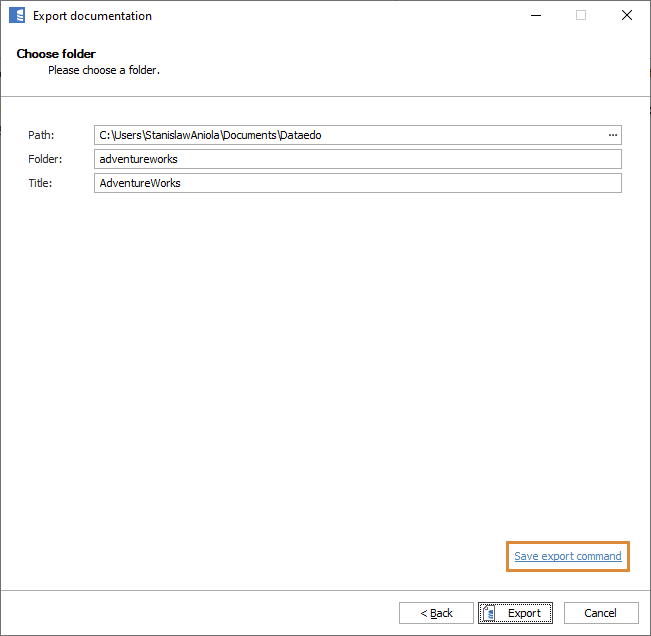
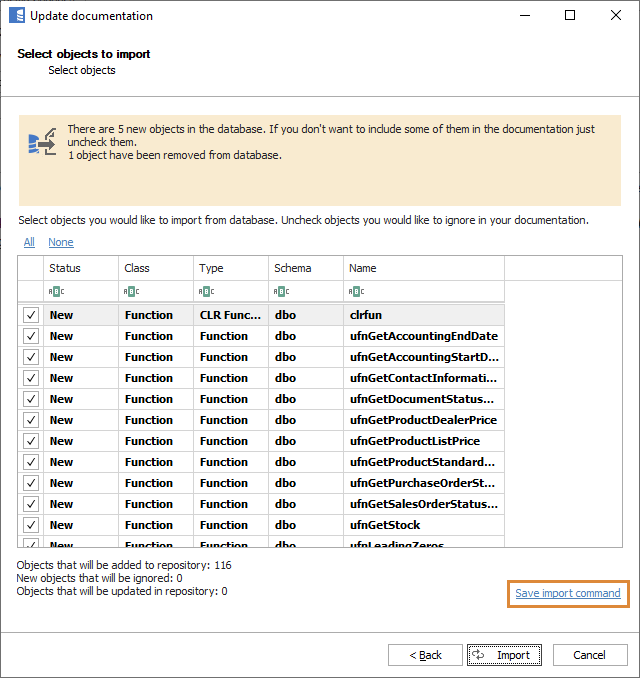
You can create a command file by clicking either Save export command on the Export documentation window (click Export in the ribbon) or Save import command on the Update documentation window (click Import changes in the ribbon).
Dataedo command files are XML-based and can be read and edited with any text editor. Command files have a .dataedocmd extension.
The file is divided into two main parts - Settings, which contains the log file path, and Commands, which contains the actual operation to be executed - currently either export or update commands.
Export command file
This file will export your documentation to PDF, HTML, or Excel.
Generating file
To create an export command file, click Save export command on the Export documentation window.
File structure
Settings > LogFile > Path node specifies the path and name of the log of the operation. If the path is not specified, it will be placed in the same folder as the command file. If no filename is specified, the log will be placed in %USERPROFILE%\Documents\Dataedo\Logs\log YYYY-MM-DD HHmmSS.log.
Commands > Export > Overwrite specifies whether the output file should be replaced if it already exists. If set to false, the file will be saved with a new name, with the added date.
Commands > Export > OutputPath node specifies the path and name of the output file (or folder if exporting HTML documentation). If no path is specified, the output file will be created in the same folder as the command file. If no filename is specified, the export will fail.
Example structure of an export command file is:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<DataedoCommands xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" Version="1.0">
<!-- Visit https://dataedo.com/docs/run-dataedo-from-command-line for more information about Dataedo command line scripts. -->
<Settings>
<LogFile>
<Path>Dataedo Import from AdventureWorks {DateTime:yyyy-MM-dd}.log</Path>
</LogFile>
</Settings>
<Commands>
<Import IsEnabled="true">
<!-- Repository connection -->
<SqlServerRepository>
<Timeout xsi:nil="true" />
<Host>hermes</Host>
<Database>dataedo</Database>
<AuthenticationType>WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION</AuthenticationType>
</SqlServerRepository>
<!-- Updated documentation: AdventureWorks -->
<RepositoryDocumentationId xsi:nil="true" />
<FullReimport>false</FullReimport>
<!-- Database connection -->
<SqlServerSourceDatabase>
<Timeout>120</Timeout>
<Host>hermes</Host>
<Database>AdventureWorks</Database>
<AuthenticationType>WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION</AuthenticationType>
</SqlServerSourceDatabase>
<FilterRules>
<Rule>
<RuleType>Include</RuleType>
<ObjectType>Any</ObjectType>
<Schema />
<Name />
</Rule>
</FilterRules>
</Import>
</Commands>
</DataedoCommands>
Update command file
This file will update your documentation from the source database.
Generating file
To create an update command file, click Save import command on the Update documentation window.
File structure
Settings > LogFile > Path node specifies the path and name of the log of the operation. If the path is not specified, it will be placed in the same folder as the command file. If no filename is specified, the log will be placed in %USERPROFILE%\Documents\Dataedo\Logs\log YYYY-MM-DD HHmmSS.log.
Commands > Import > SqlServerCeRepository > Path node specifies the path of the Dataedo repository file, which will have the documentation updated.
Commands > Import > SqlServerRepository > Host node specifies the host address of the Dataedo repository, which will have the documentation updated.
Commands > Import > SqlServerRepository > Database node specifies the Dataedo repository database, which will have the documentation updated.
Commands > Import > MySQLSourceDatabase node specifies the MySQL source database server, from which metadata will be imported.
Commands > Import > SqlServerSourceDatabase node specifies the SQL Server source database server, from which metadata will be imported.
Commands > Import > OracleSourceDatabase node specifies the Oracle source database server, from which metadata will be imported.
Example structure of an import command file is:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<DataedoCommands xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" Version="1.0">
<!-- Visit https://dataedo.com/docs/run-dataedo-from-command-line for more information about Dataedo command line scripts. -->
<Settings>
<LogFile>
<Path>Dataedo Import from AdventureWorks {DateTime:yyyy-MM-dd}.log</Path>
</LogFile>
</Settings>
<Commands>
<Import IsEnabled="true">
<!-- Repository connection -->
<SqlServerRepository>
<Timeout xsi:nil="true" />
<Host>hermes</Host>
<Database>dataedo</Database>
<AuthenticationType>WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION</AuthenticationType>
</SqlServerRepository>
<!-- Updated documentation: AdventureWorks -->
<RepositoryDocumentationId xsi:nil="true" />
<FullReimport>false</FullReimport>
<!-- Database connection -->
<SqlServerSourceDatabase>
<Timeout>120</Timeout>
<Host>hermes</Host>
<Database>AdventureWorks</Database>
<AuthenticationType>WINDOWS_AUTHENTICATION</AuthenticationType>
</SqlServerSourceDatabase>
<FilterRules>
<Rule>
<RuleType>Include</RuleType>
<ObjectType>Any</ObjectType>
<Schema />
<Name />
</Rule>
</FilterRules>
</Import>
</Commands>
</DataedoCommands>
Variables in paths or filenames
There are a few special strings which will be replaced by Dataedo if put in the Path or OutputPath node.
{DateTime:yyyy-MM-dd} will be replaced by the current date.
{DateTime:yyyy-MM-dd hhmmss} will be replaced by the current date and time.
{MyDocuments} will be replaced by the Dataedo directory in the user's My documents folder.
Executing a command
Executing from command line
To execute a command file, open the command line (cmd) and type in:
"[Dataedo executable path and filename]" /dataedocmd "[Dataedo command file path and filename]".
For instance:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Dataedo 7\Dataedo7.exe" /dataedocmd "C:\DataedoCmd\MyUpdate.dataedocmd"
You can also place the same line in a batch file.
Executing from Explorer
You can also immediately run the command by double-clicking on it. This requires that the file is associated with Dataedo if it was installed (not just unzipped) on your machine.
Exit code
After completing the operation, Dataedo returns an exit code. You can check it by typing echo Exit code: %errorlevel%. You can also use the %errorlevel% variable in your batch file.
Possible exit codes:
-
0 - operation finished successfully
-
1 or more - count of commands that failed
-
-1 - unexpected error, check the log file
-
-2 - command file does not exist
-
-3 - invalid command file.
Log file
Executing a command creates a log file in the specified path. If you don't see a log file after executing the command, either its path or filename was invalid or you do not have write access to it. In this case, it will be placed in %USERPROFILE%\Documents\Dataedo\Logs\log YYYY-MM-DD HHmmSS.log.
Scheduling
You can create a task in Windows Scheduler which will automatically execute your Dataedo command file according to the set schedule.
-
Open Windows Scheduler
-
Click Create a task in the Actions tab
-
Set the General tab and Triggers tab as you like
-
Click New in the Actions tab
-
Set the File/script box to the Dataedo executable location
-
Type in /dataedocmd followed by the path and filename of your Dataedo command file in double quotes in the Arguments box
-
Confirm the changes
This way your command file will be executed according to the schedule.

